|
Meniscal lesion
Definition
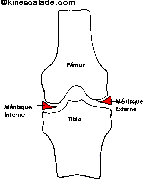
Menisci of the knee are fibrocartilage elements whose role is to split the constraints which are transmitted from the thighbone to the shinbone (fig 1).
They can break lengthways or transversely (fig 2).
In some cases, the meniscus can be cracked without the person feeling it.
In other cases, the fracture can occur with an acute pain and a very audible crack.
An important (or persistent) bulge is often linked to it
 |
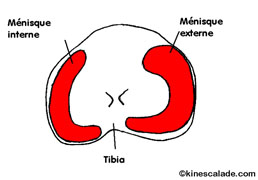 |
Fig 1: Frontal cut
of the knee’s articulation |
Fig 2: Superior view of the tibial tray |
Mechanism of the lesion
Menisci can get stuck between the thighbone and the shinbone and be subjected to more important constraints than their mechanical resistance.
It can occur during movements when the knee is flexed to its maximum, with a more or less important rotation of the shinbone.
When the person stands up straight on one leg (slab movement) (fig 3), the quadriceps have to contract strongly while the position of the knee in hyper flexing makes it impossible for the hamstrings to play their role: controlling the position of the menisci.
A fall (in bouldering) can seriously damage these structures.

Fig 3: Knee movement in maximum flexing
Prevention
Technique correction:
Avoid standing up straight on one leg.
When bouldering, spotting will be essential for a good reception.
Correction of the physical preparation:
All the exercises to warm up, to stretch and to strengthen the muscles have to respect the physiological axis of flexing and extending of the knee.
A good warm up and a good waking of the sensory receptors through active stretching techniques can prevent wrong movements of the menisci.
Treatment
Apply an ice pack right after the accident 3 times per day till the oedema disappears.
See a sport doctor. According to the functional inconvenience, a surgical intervention to remove one part of the meniscus might prove necessary.
Successful rehabilitation might allow you to take up climbing again.
|

